Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation that results in the long-term swelling of the eyelids and eyelash follicles. It may be caused by seborrheic dermatitis, acne, bacterial infection, allergic reaction or poor eyelid hygiene. The eyelids crust, flake, scale or redden, and the smooth inside lining of the lids may become rough.
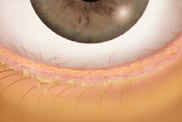
In more serious cases, sores can form when the crusting skin is removed, the eyelashes may fall out, the eyelids can deform, or the infection can spread to the cornea. Patients often suffer from excessive tearing.
Treatment and preventative care for blepharitis involves thorough but gentle cleaning of the eyelids, face and scalp. This may be combined with antibiotics if a bacterial infection is causing or contributing to the problems.
Uveitis
Uveitis is a general term that refers to an inflammation or swelling of the eye's structures responsible for its blood supply. This condition can occur as an autoimmune disorder which causes the body to attack its own tissues or as a result of injury, infection, or exposure to toxins.
Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, which is known as the uvea. The uvea is composed of three structures;
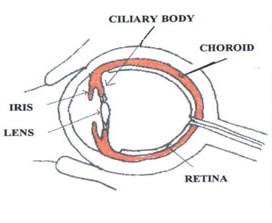
- The iris is the colored structure of the eye surrounding the pupil
- The ciliary body is the muscle that supports the iris and focuses the lens
- The choroid is the layer containing the eye's blood vessels located between the inner retina and the sclera (the white of the eye)
Uveitis Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of uveitis depend on whether it is anterior, intermediate, posterior or diffuse in location.
Anterior
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Redness around the limbus
- Pain that may range from aching or soreness to intense discomfort
- Small pupil
- Tearing
- Elevated intraocular pressure
Intermediate
- Often affects both eyes
- Floaters
- Blurred vision
Posterior
- Blurred vision
- Pain (if the optic nerve is involved)
Diffuse
- Combination of symptoms from anterior, intermediate, and posterior uveitis
Treatment of Uveitis
Prompt treatment is necessary to minimize any loss of vision. Eye drops, especially steroids and pupil dilators, are medications used to reduce inflammation and pain.
For deeper inflammation, oral medication or injections may be necessary. Complications such as glaucoma (high pressure in the eye), cataracts (clouding of the lens of the eye), or new blood vessel formation (neovascularization), also may need treatment in the course of the disease. If complications are advanced, conventional or laser surgery may be necessary.
Uveitis in the front and middle part of the eye (iritis or cyclitis) is commonly more sudden in onset, generally lasting six to eight weeks, and in the early stages can usually be controlled by the frequent use of drops. Often, this type of uveitis cannot be given a specific cause.
Uveitis in the back part of the eye (choroiditis) is commonly slower in onset and may last longer, and is often more difficult to treat.